| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
Cellulose microcrystalline
CAS:9004-34-6 |
|
 |
Hydroxyethyl cellulose
CAS:9004-62-0 |
|
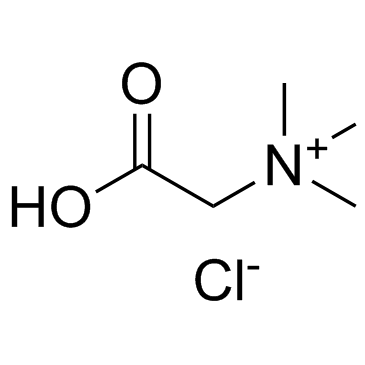 |
Betaine Hydrochloride
CAS:590-46-5 |
|
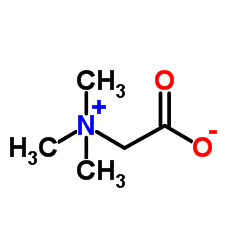 |
Betaine
CAS:107-43-7 |