| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
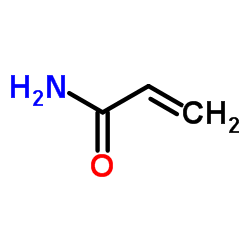 |
Acrylamide Crystals
CAS:79-06-1 |
|
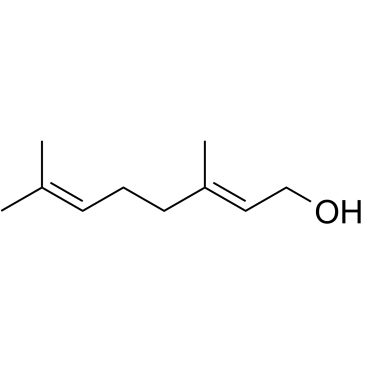 |
Geraniol
CAS:106-24-1 |
|
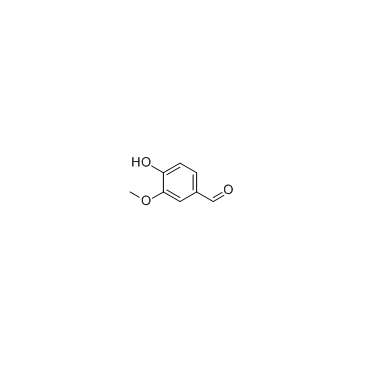 |
Vanillin
CAS:121-33-5 |
|
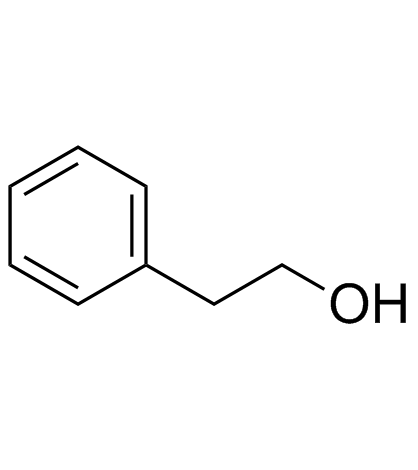 |
Phenethyl alcohol
CAS:60-12-8 |
|
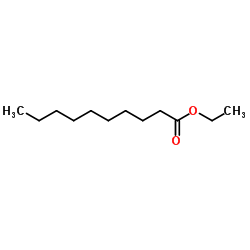 |
Ethyl caprate
CAS:110-38-3 |
|
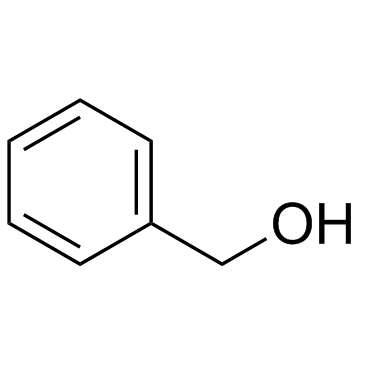 |
Benzyl alcohol
CAS:100-51-6 |
|
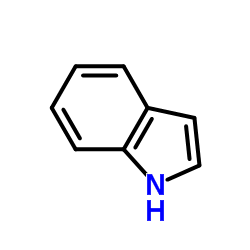 |
Indole
CAS:120-72-9 |
|
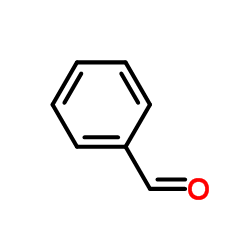 |
Benzaldehyde
CAS:100-52-7 |
|
 |
Methyl salicylate
CAS:119-36-8 |