| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
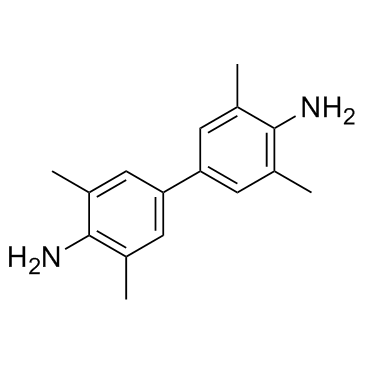 |
Tetramethylbenzidine
CAS:54827-17-7 |
|
 |
Sodium deoxycholate
CAS:302-95-4 |
|
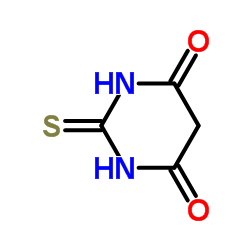 |
4,6-Dihydroxy-2-mercaptopyrimidine
CAS:504-17-6 |
|
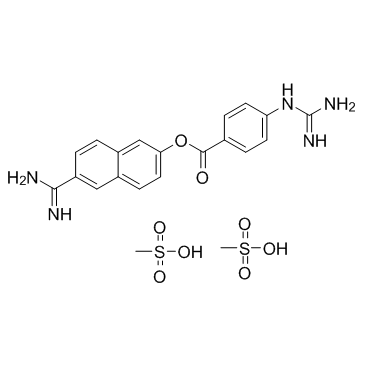 |
Nafamostat mesylate
CAS:82956-11-4 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |