| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
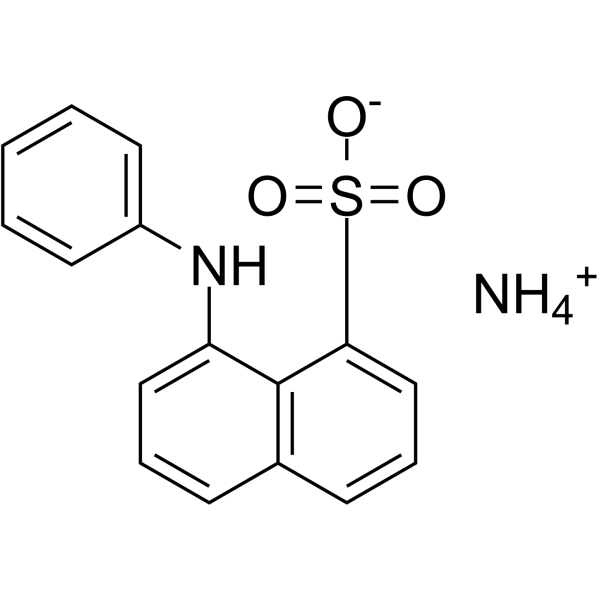 |
1-ANILINONAPHTHALENE-8-SULFONIC ACID AMMONIUM SALT
CAS:28836-03-5 |
|
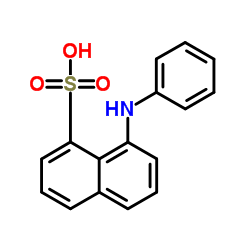 |
8-Anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid
CAS:82-76-8 |
|
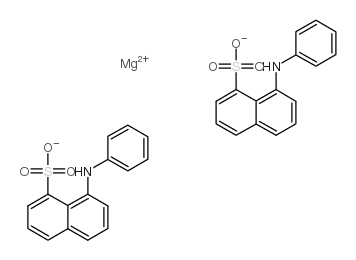 |
8-Anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid magnesium salt
CAS:18108-68-4 |
|
 |
Conalbumin, from chicken egg white
CAS:1391-06-6 |