Reversal of P-glycoprotein overexpression by Ginkgo biloba extract in the brains of pentylenetetrazole-kindled and phenytoin-treated mice.
Ce Zhang, Qing Fan, Shu-Liang Chen, Hui Ma
Index: Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 31 , 398-404, (2015)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the combined effects of Ginkgo biloba extract and phenytoin (PHT) sodium as a dose regimen simulating the clinical treatment of patients with epilepsy, on P-glycoprotein (P-GP) overexpression in a pentylenetetrazole-kindled mouse model of epilepsy. Epilepsy was induced by intraperitoneal administration of pentylenetetrazole (40 mg/kg) for 7 days followed by intragastric administration of PHT (40 mg/kg) for 14 days. Thirty mice that developed seizures were randomly divided into three groups and administered PHT as well as the following treatments: saline (negative control); verapamil (20 mg/kg, positive control); and G. biloba (30 mg/kg). Seizure severity was recorded 30 minutes after treatment on Day 4 of drug administration, after which the mice were euthanized, and their brains isolated. Western blots and immunohistochemistry were performed to analyze the expression of P-GP and caspase-3, respectively, in the brain tissue. High-performance liquid chromatography was used to measure the concentrations of PHT in the brains of the treated mice. After 4 consecutive days of treatment, the seizure severity in the mice in the G. biloba extract group was more significantly reduced than the seizure severity in the saline control group, and a significant difference was observed between the G. biloba extract and verapamil control groups (p < 0.05). P-GP expression in the brain more significantly decreased in the mice treated with G. biloba extract and verapamil than it did in the saline-treated control group (p < 0.05). Compared with the saline-treated control group, the mice treated with G. biloba extract and verapamil showed significantly increased brain PHT concentrations (p < 0.05). Furthermore, caspase-3 expression in the brain tissue of the G. biloba extract group was significantly lower than that in the vehicle control group (p < 0.05); this finding demonstrated the neuroprotective effects of G. biloba. Therefore, this study showed that treatment with G. biloba extract in combination with PHT prevented the upregulation of P-GP expression in mice. Moreover, G. biloba extract decreased seizure severity in pentylenetetrazole-kindled/PHT-treated mice through a mechanism that might be related to the reduction of P-GP expression in the brain.Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier Taiwan.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
CH4O | |
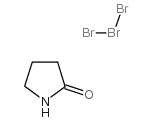 |
pyrrolidone hydrotribromide
CAS:22580-55-8 |
C4H7Br3NO |
|
BBS4 directly affects proliferation and differentiation of a...
2014-09-01 [Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71(17) , 3381-92, (2014)] |
|
Urinary metabolic fingerprinting of mice with diet-induced m...
2014-09-26 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1361 , 265-76, (2014)] |
|
Biomolecular imaging with a C60-SIMS/MALDI dual ion source h...
2014-11-01 [J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 25(11) , 1897-907, (2014)] |
|
Synergistic activity of tenofovir and nevirapine combination...
2014-10-01 [Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 88(2) , 406-14, (2014)] |
|
Antinematode activity of Violacein and the role of the insul...
2014-01-01 [PLoS ONE 9(10) , e109201, (2014)] |