| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
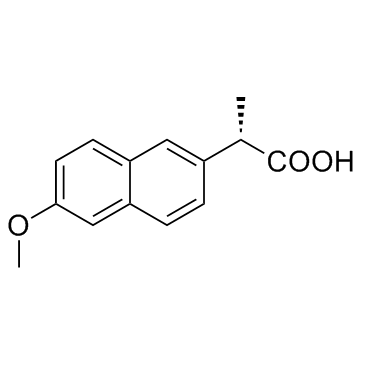 |
Naproxen
CAS:22204-53-1 |
|
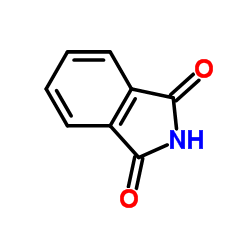 |
O-Phthalimide
CAS:85-41-6 |
|
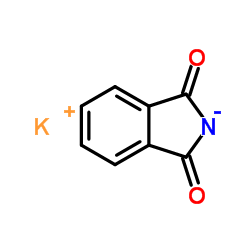 |
Potassium phthalimide
CAS:1074-82-4 |
|
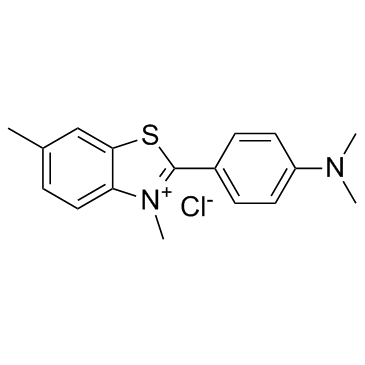 |
Thioflavine T
CAS:2390-54-7 |