| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
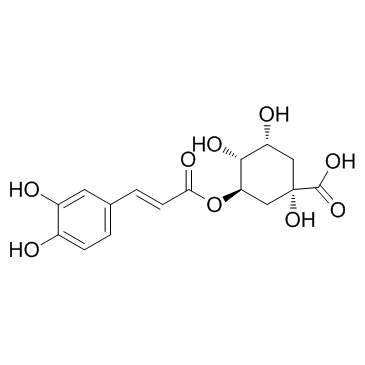 |
Chlorogenic acid
CAS:327-97-9 |
|
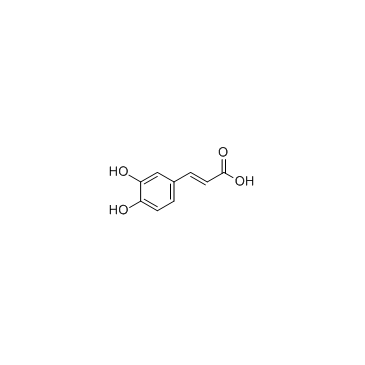 |
Caffeic acid
CAS:331-39-5 |
|
 |
trans-4-Hydroxycinnamic acid
CAS:501-98-4 |
|
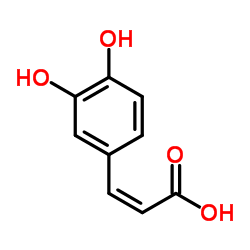 |
caffeic acid
CAS:501-16-6 |