| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Formaldehyde
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
 |
3-(Trimethoxysilyl)-1-propanamine
CAS:13822-56-5 |
|
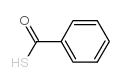 |
Thiobenzoic acid
CAS:98-91-9 |
|
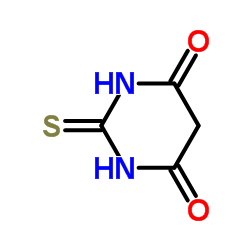 |
4,6-Dihydroxy-2-mercaptopyrimidine
CAS:504-17-6 |
|
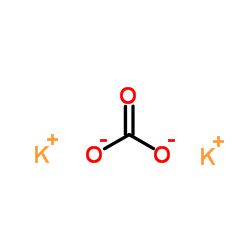 |
Potassium carbonate
CAS:584-08-7 |