| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
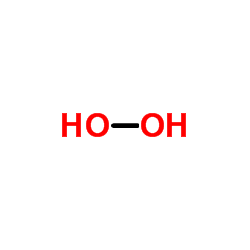 |
Hydrogen peroxide
CAS:7722-84-1 |
|
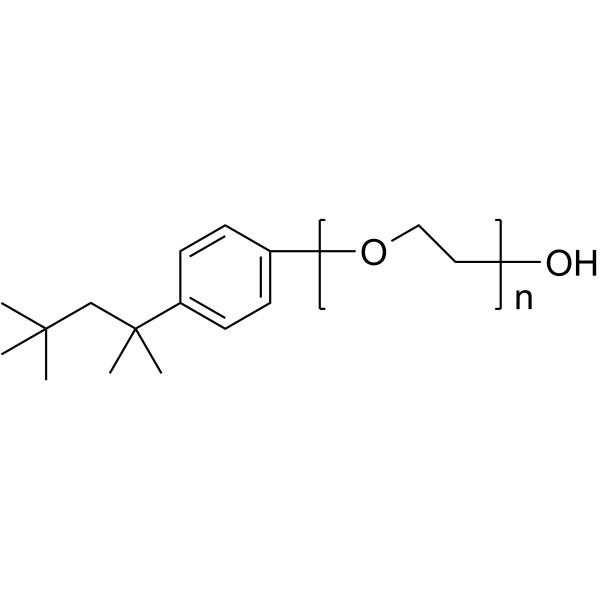 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
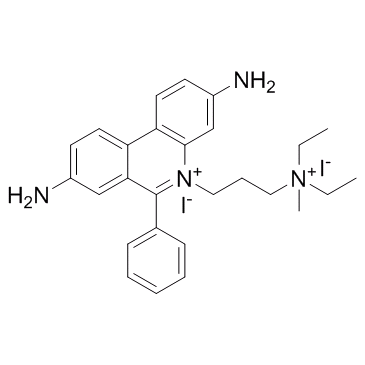 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |
|
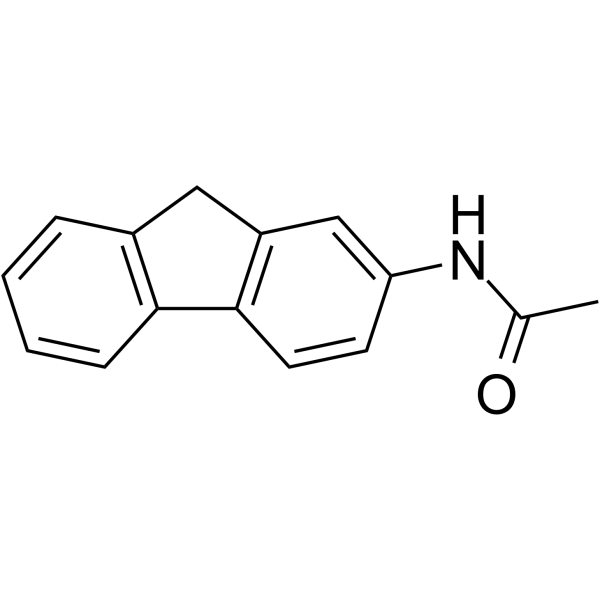 |
2-Acetamidofluorene
CAS:53-96-3 |