| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
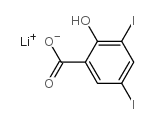 |
LITHIUM 3,5-DIIODOSALICYLATE
CAS:653-14-5 |
|
 |
3,5-Diiodosalicylic acid
CAS:133-91-5 |
|
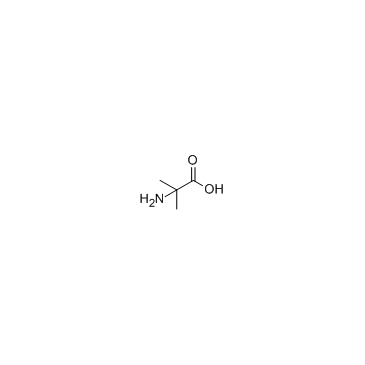 |
2-Aminoisobutyric acid
CAS:62-57-7 |