| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
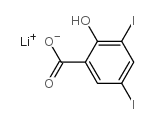 |
LITHIUM 3,5-DIIODOSALICYLATE
CAS:653-14-5 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
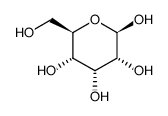 |
Beta-D-allose
CAS:7283-09-2 |