| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
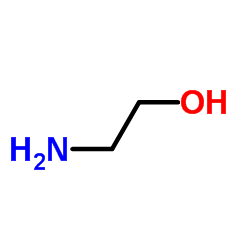 |
2-Aminoethanol
CAS:141-43-5 |
|
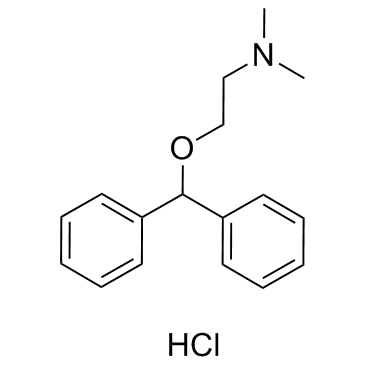 |
Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride
CAS:147-24-0 |
|
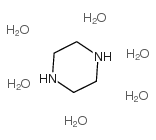 |
Piperazine Hexahydrate
CAS:142-63-2 |
|
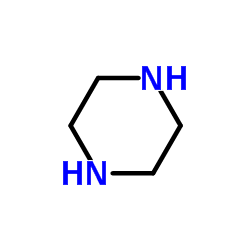 |
Piperazine
CAS:110-85-0 |