| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
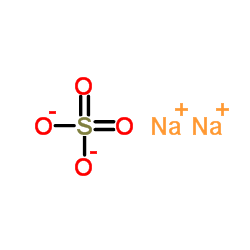 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
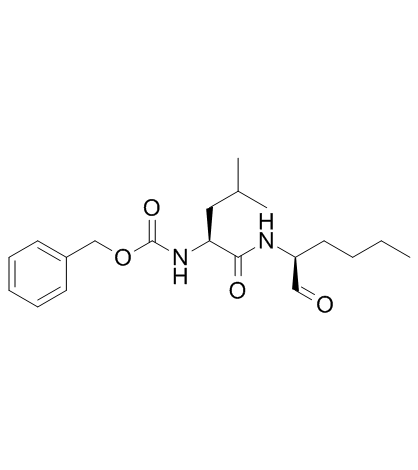 |
calpeptin
CAS:117591-20-5 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
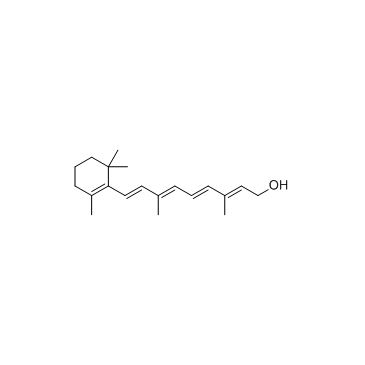 |
Vitamin A
CAS:68-26-8 |