| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
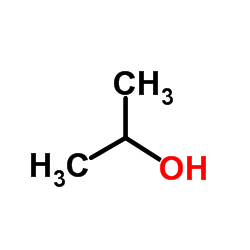 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
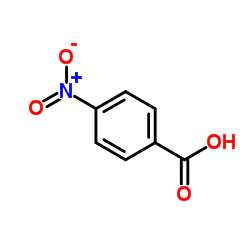 |
4-Nitrobenzoic acid
CAS:62-23-7 |
|
 |
DEBRISOQUIN SULFATE
CAS:581-88-4 |