| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
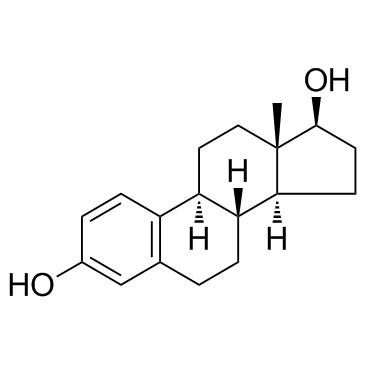 |
beta-Estradiol
CAS:50-28-2 |
|
 |
Glycine
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
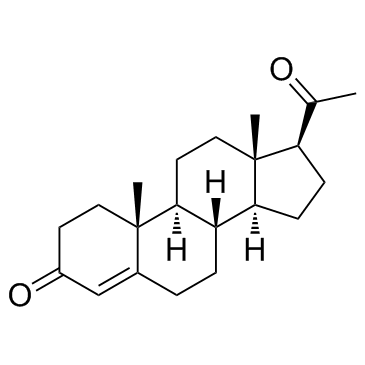 |
Progesterone
CAS:57-83-0 |
|
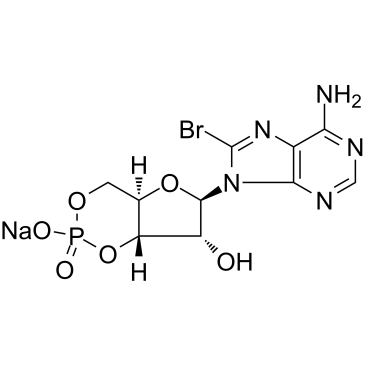 |
8-Bromo-cAMP sodium salt
CAS:76939-46-3 |
|
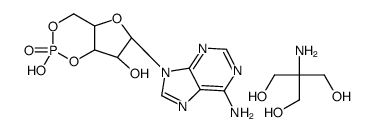 |
ADENOSINE 3':5'-CYCLIC MONOPHOSPHATE TRIS SALT
CAS:102029-77-6 |
|
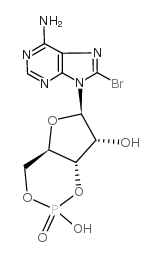 |
8-bromo-Cyclic AMP
CAS:23583-48-4 |
|
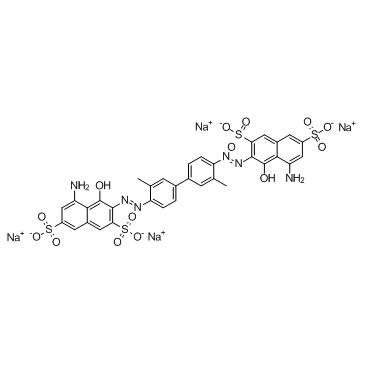 |
Direct Blue 14
CAS:72-57-1 |
|
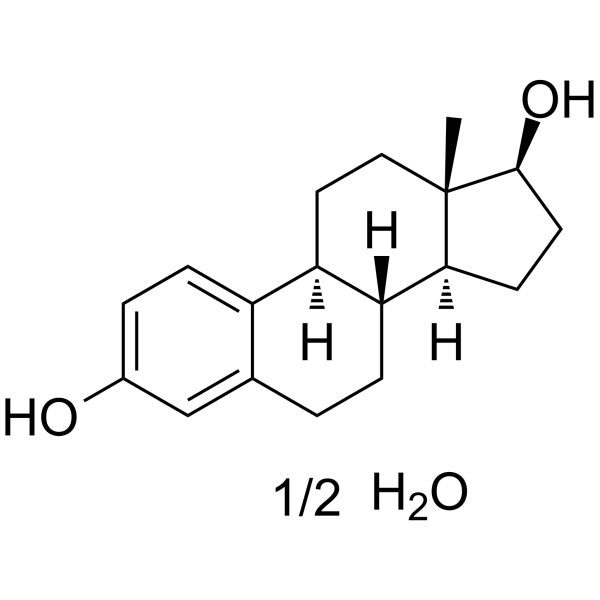 |
ESTRADIOL HEMIHYDRATE
CAS:35380-71-3 |
|
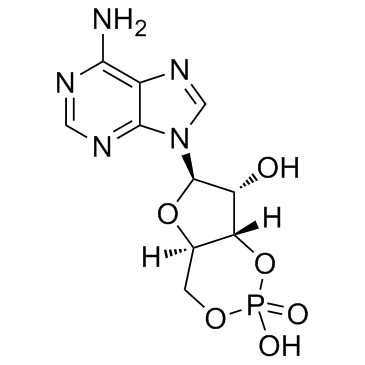 |
Adenosine cyclophosphate
CAS:60-92-4 |