| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
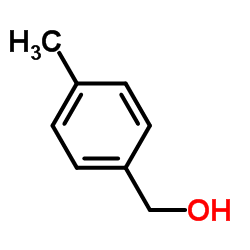 |
p-tolylmethanol
CAS:589-18-4 |
|
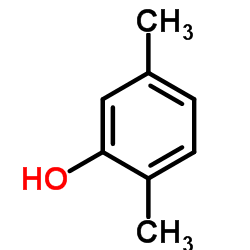 |
2,5-Dimethylphenol
CAS:95-87-4 |