Synthesis of oligosaccharides by bacterial enzymes.
K F Johnson
Index: Glycoconj. J. 16(2) , 141-6, (1999)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Many human pathogens initiate disease by utilizing their microbial adhesin proteins to attach to glycoconjugates on host cell mucosal surfaces. Soluble oligosaccharides of identical or similar structure to these naturally occurring ligands can both prevent bacterial attachment as well as mediate the release of attached bacteria. Since it has not been possible to isolate large quantities of these compounds, we have developed enzyme-based technologies to synthesize several relevant human oligosaccharides. Using cloned bacterial glycosyltransferases, we can synthesize several hundred grams of these oligosaccharides at a time. The availability of these large quantities will allow these compounds to be tested as anti-adhesive pharmaceutical agents as well as lead to expanded practical applications.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
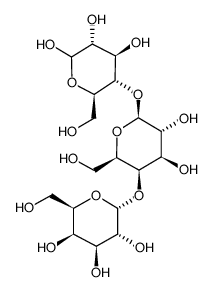 |
Globotriose
CAS:66580-68-5 |
C18H32O16 |
|
Carbosilane dendrimers bearing globotriaoses: syntheses of g...
2006-08-01 [Biomacromolecules 7(8) , 2274-83, (2006)] |
|
Efficient chemoenzymatic synthesis of globotriose and its de...
2002-06-05 [Carbohydr. Res. 337(11) , 969-76, (2002)] |
|
Structural analysis of the interaction between Shiga toxin B...
2006-03-01 [Infect. Immun. 74(3) , 1984-8, (2006)] |
|
Determination of the cell adhesion specificity of Streptococ...
1999-01-01 [Glycoconj. J. 16(1) , 67-71, (1999)] |
|
Structure of extended lipopolysaccharide glycoforms containi...
2003-04-22 [Biochemistry 42(15) , 4463-75, (2003)] |