| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
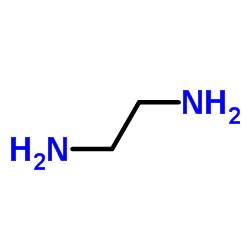 |
1,2-Ethanediamine
CAS:107-15-3 |
|
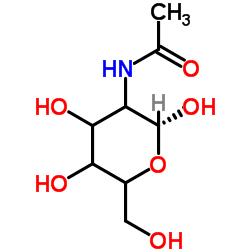 |
chitin
CAS:1398-61-4 |
|
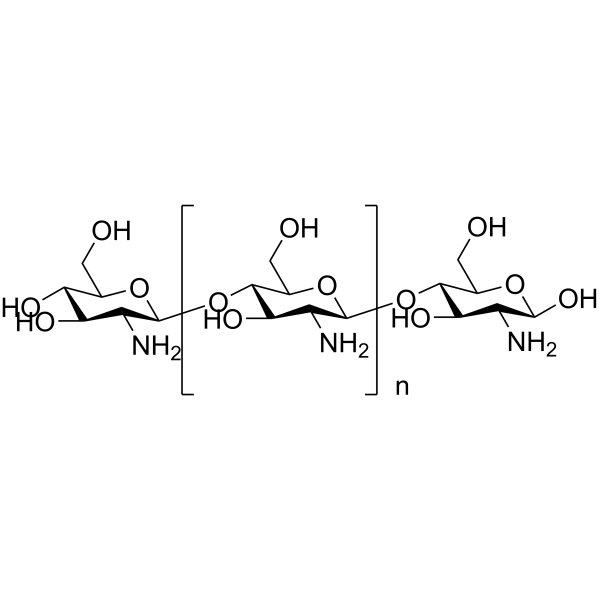 |
Chitosan
CAS:9012-76-4 |
|
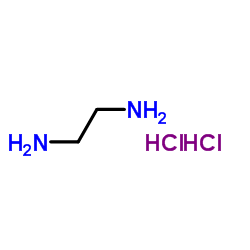 |
ethane-1,2-diaminium dichloride
CAS:333-18-6 |