| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
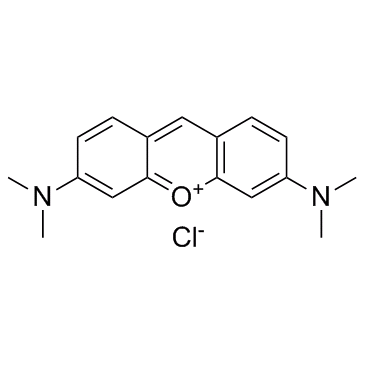 |
Pyronin Y
CAS:92-32-0 |
|
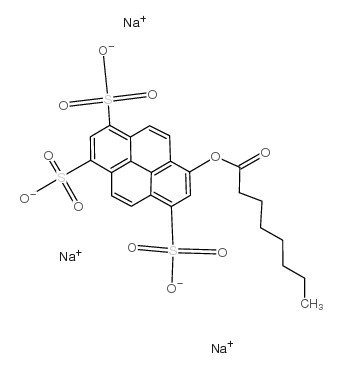 |
8-Octanoyloxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium salt
CAS:115787-84-3 |