| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
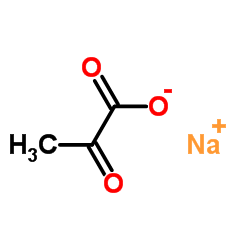 |
Sodium 2-oxopropanoate
CAS:113-24-6 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
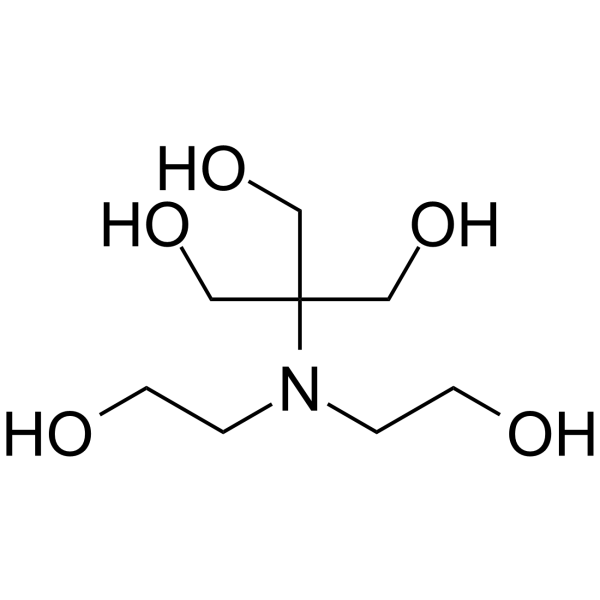 |
Bis-tris methane
CAS:6976-37-0 |
|
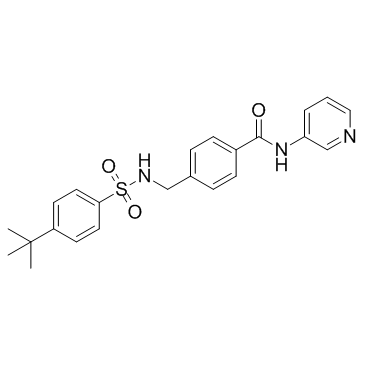 |
STF 31
CAS:724741-75-7 |