| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
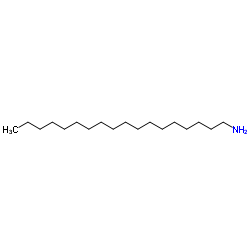 |
Octadecanamine
CAS:124-30-1 |
|
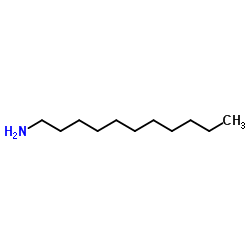 |
1-Undecanamine
CAS:7307-55-3 |
|
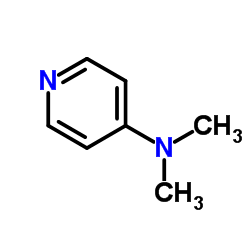 |
4-Dimethylaminopyridine
CAS:1122-58-3 |
|
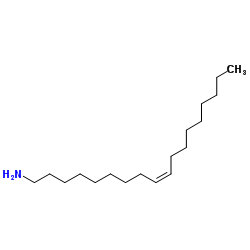 |
Oleylamine
CAS:112-90-3 |
|
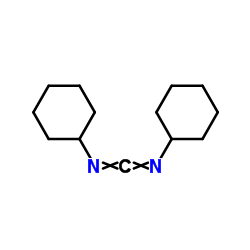 |
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
CAS:538-75-0 |