| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
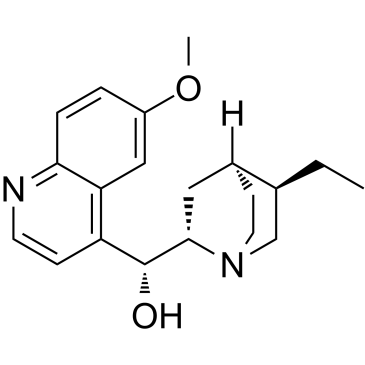 |
dihydroquinine
CAS:522-66-7 |
|
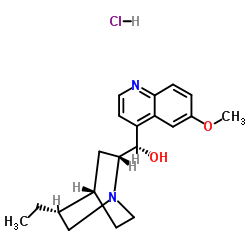 |
TCMDC-125509
CAS:1476-98-8 |