| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
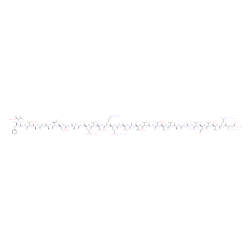 |
α-Synuclein (61-95) (human) trifluoroacetate salt
CAS:154040-19-4 |
|
 |
Glycine
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
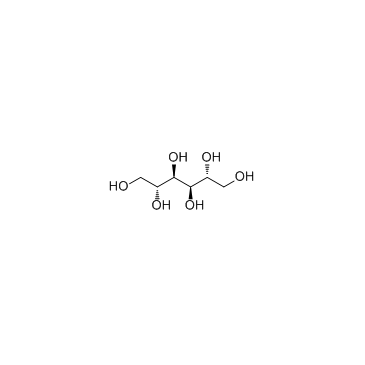 |
D-Mannitol
CAS:69-65-8 |
|
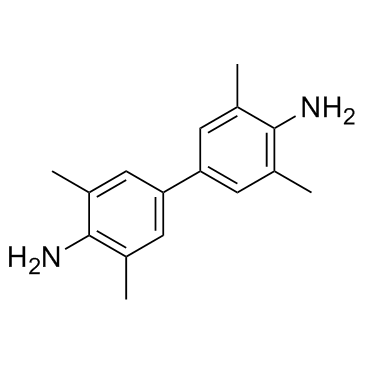 |
Tetramethylbenzidine
CAS:54827-17-7 |
|
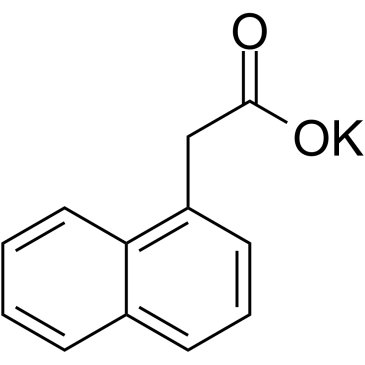 |
Potassium 1-naphthylacetate
CAS:15165-79-4 |
|
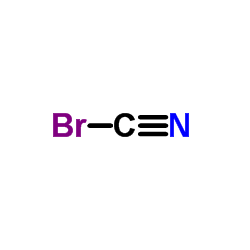 |
Cyanogen bromide
CAS:506-68-3 |