| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
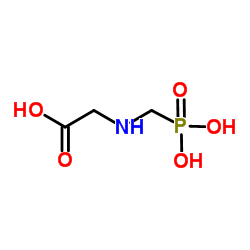 |
Glyphosate
CAS:1071-83-6 |
|
 |
Glycine
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
 |
CHLOROPHYLL A
CAS:479-61-8 |
|
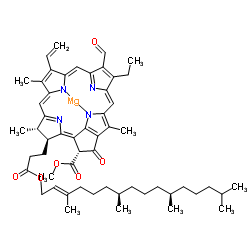 |
b-Chlorophyll
CAS:519-62-0 |
|
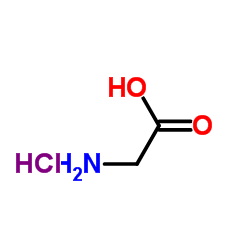 |
Glycine HCl
CAS:6000-43-7 |