| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
D-3-phenyllactic acid
CAS:7326-19-4 |
|
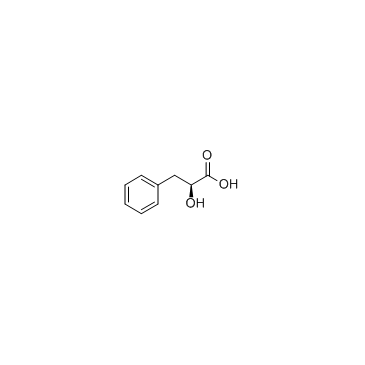 |
L-(-)-3-Phenyllactic acid
CAS:20312-36-1 |
|
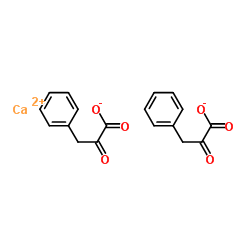 |
Calcium phenylpyruvate
CAS:51828-93-4 |
|
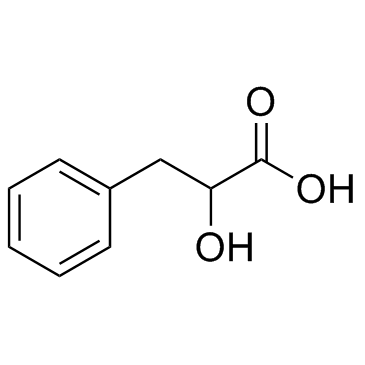 |
D-3-phenyllactic acid
CAS:828-01-3 |
|
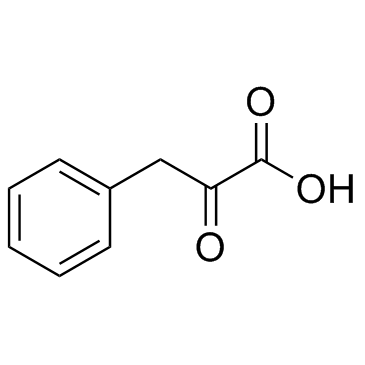 |
2-Oxo-3-phenylpropanoic acid
CAS:156-06-9 |
|
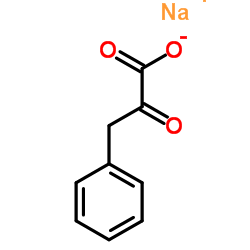 |
Sodium 2-oxo-3-phenylpropanoate
CAS:114-76-1 |