| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
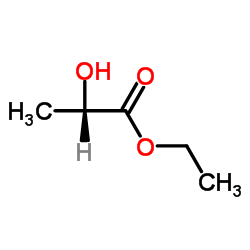 |
(−)-Ethyl L-lactate
CAS:687-47-8 |
|
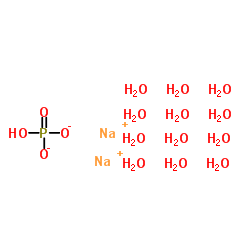 |
Disodium phosphate dodecahydrate
CAS:10039-32-4 |
|
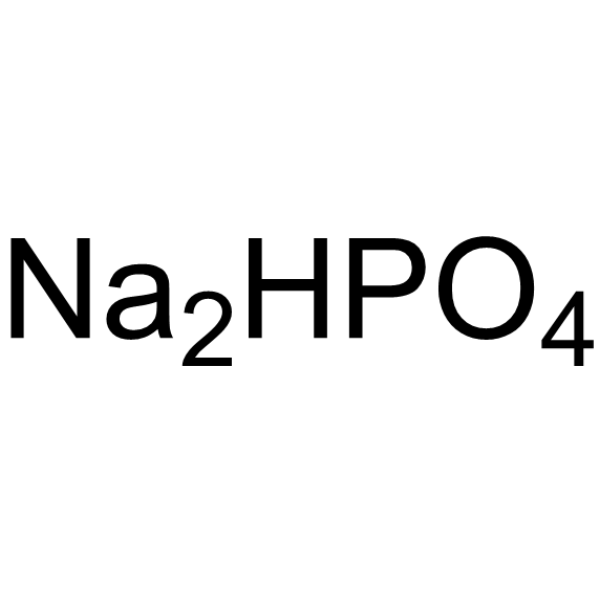 |
Disodium hydrogenorthophosphate
CAS:7558-79-4 |
|
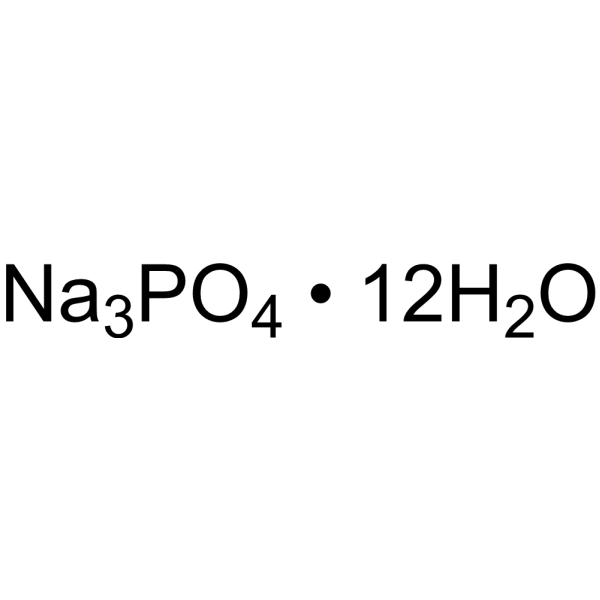 |
Trisodium phosphate dodecahydrate
CAS:10101-89-0 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
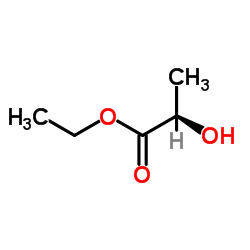 |
(R)-ethyl 2-hydroxypropanoate
CAS:7699-00-5 |
|
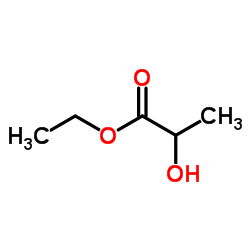 |
Ethyl lactate
CAS:97-64-3 |
|
 |
sodium dihydrogenphosphate
CAS:7558-80-7 |
|
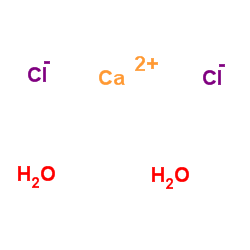 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |
|
 |
Sodium Lactate
CAS:72-17-3 |