| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
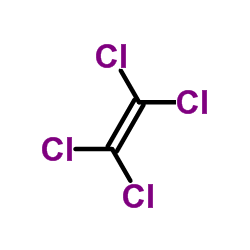 |
Tetrachloroethylene
CAS:127-18-4 |
|
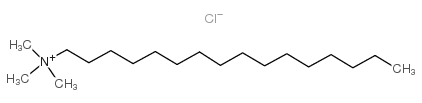 |
N-Hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride
CAS:112-02-7 |
|
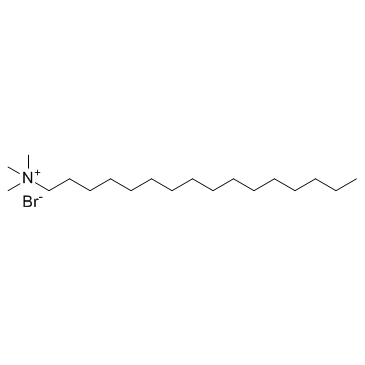 |
Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
CAS:57-09-0 |
|
 |
clay
CAS:1332-58-7 |
|
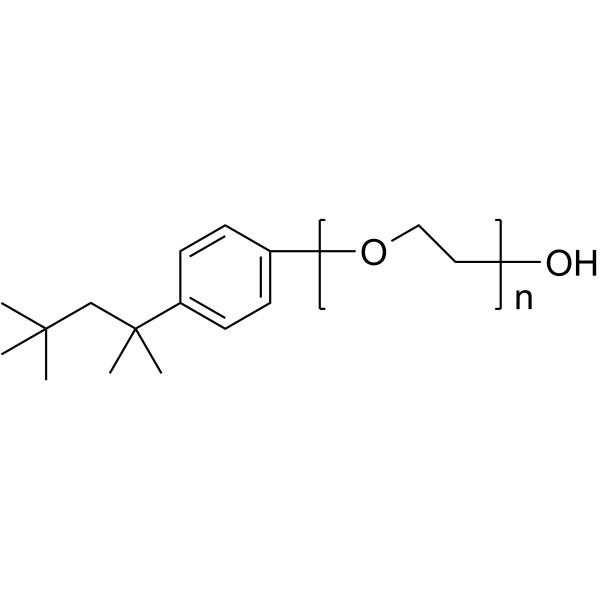 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
 |
hexadecyl-trimethyl-ammonium sulfate
CAS:68214-07-3 |