| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
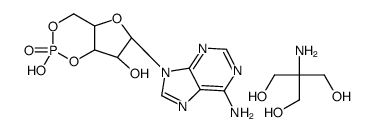 |
ADENOSINE 3':5'-CYCLIC MONOPHOSPHATE TRIS SALT
CAS:102029-77-6 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
Retinoic acid
CAS:302-79-4 |
|
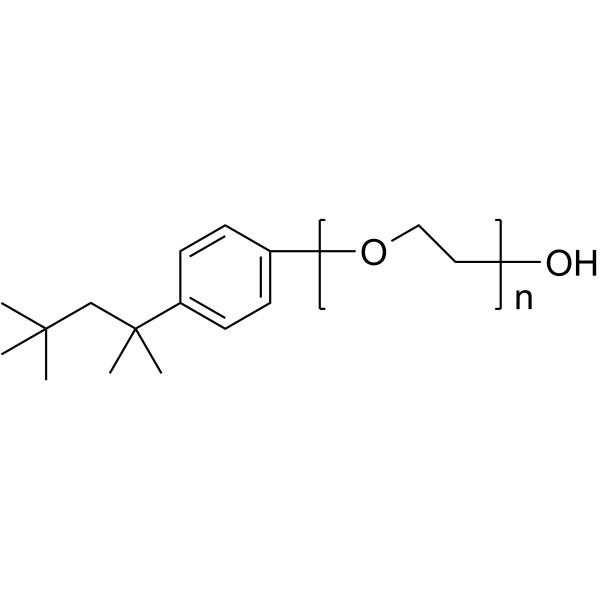 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |