| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
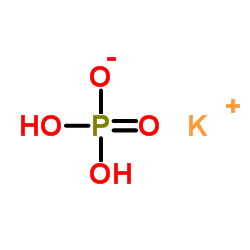 |
Monopotassium phosphate
CAS:7778-77-0 |
|
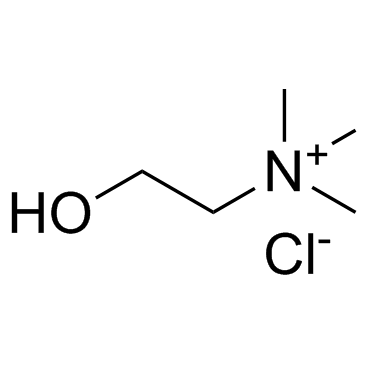 |
Choline chloride
CAS:67-48-1 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
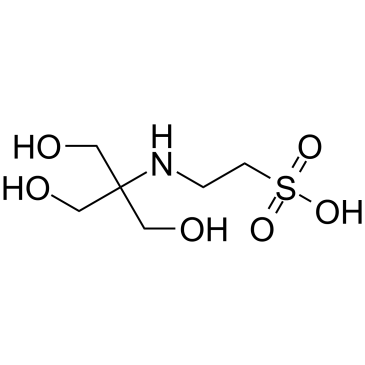 |
TES (buffer)
CAS:7365-44-8 |
|
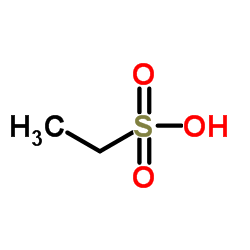 |
Ethanesulfonic acid
CAS:594-45-6 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |