| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
DL-Lysine
CAS:70-54-2 |
|
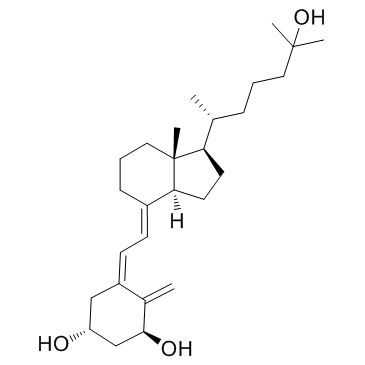 |
Calcitriol
CAS:32222-06-3 |
|
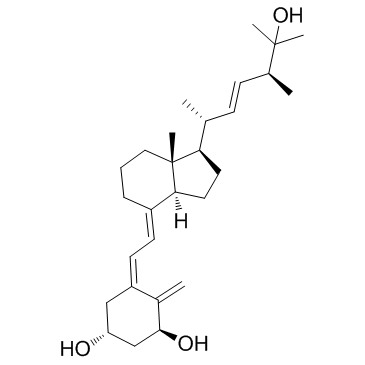 |
1-α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D2
CAS:60133-18-8 |