| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
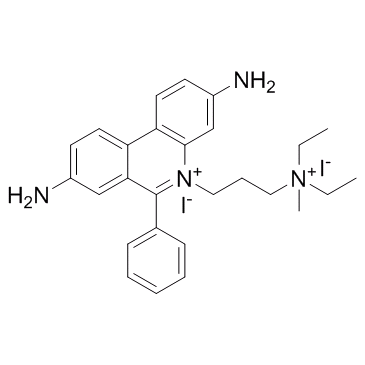 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |
|
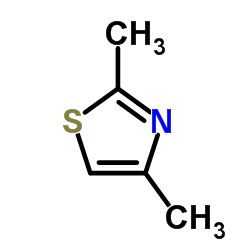 |
2.4-Dimethyl thiazole
CAS:541-58-2 |
|
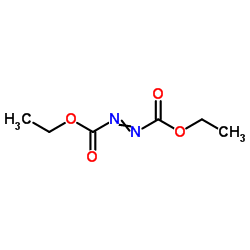 |
dead
CAS:1972-28-7 |
|
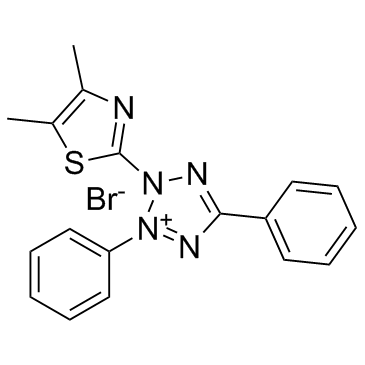 |
Thiazolyl Blue
CAS:298-93-1 |