| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
propyzamide
CAS:23950-58-5 |
|
 |
Pendimethalin
CAS:40487-42-1 |
|
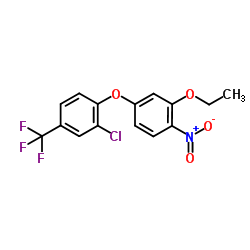 |
oxyfluorfen
CAS:42874-03-3 |
|
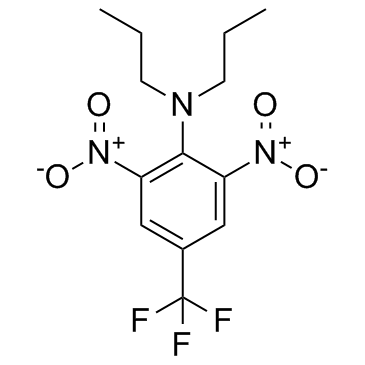 |
trifluralin
CAS:1582-09-8 |
|
 |
ethafluralin
CAS:55283-68-6 |