| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
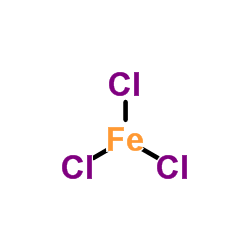 |
Ferric chloride
CAS:7705-08-0 |
|
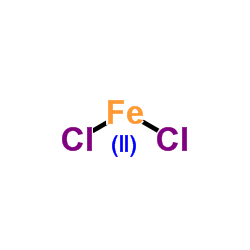 |
Ferrous chloride
CAS:7758-94-3 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
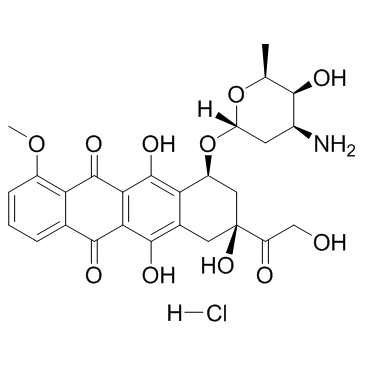 |
Doxorubicin Hydrochloride
CAS:25316-40-9 |
|
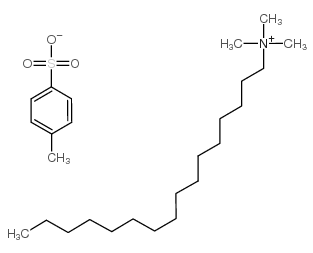 |
Hexadecyltrimethylammonium p-toluenesulfonate
CAS:138-32-9 |
|
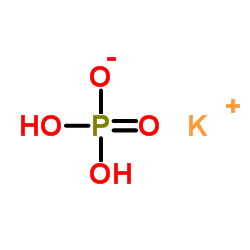 |
Monopotassium phosphate
CAS:7778-77-0 |
|
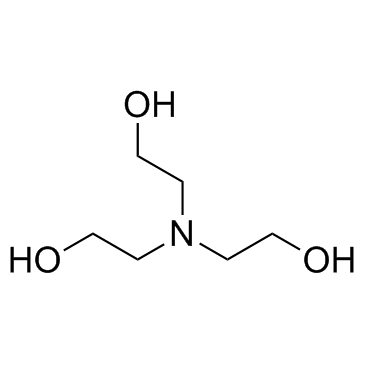 |
Triethanolamine
CAS:102-71-6 |