| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
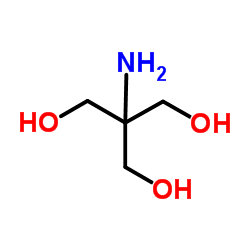 |
Trometamol
CAS:77-86-1 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
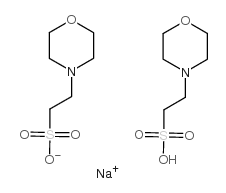 |
MES hemisodium salt
CAS:117961-21-4 |