| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
 |
Carbon
CAS:7440-44-0 |
|
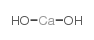 |
calcium dihydroxide
CAS:1305-62-0 |
|
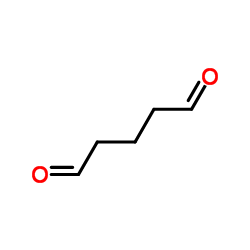 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |
|
 |
carbon black
CAS:1333-86-4 |
|
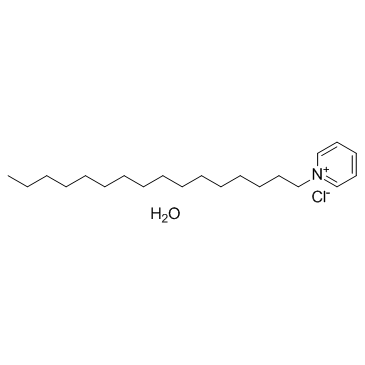 |
Cetylpyridinium chloride monohydrate
CAS:6004-24-6 |
|
 |
Dexamethasone
CAS:50-02-2 |