| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
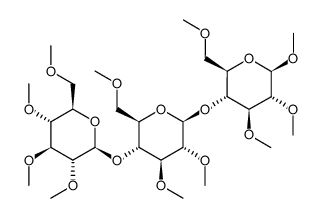 |
methyl cellulose
CAS:9004-67-5 |
|
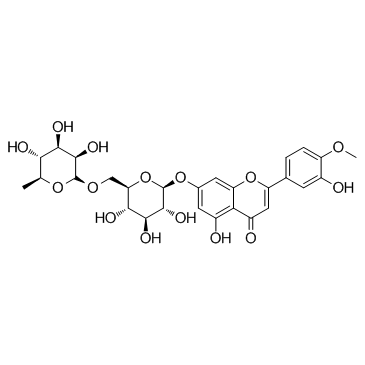 |
Diosmin
CAS:520-27-4 |
|
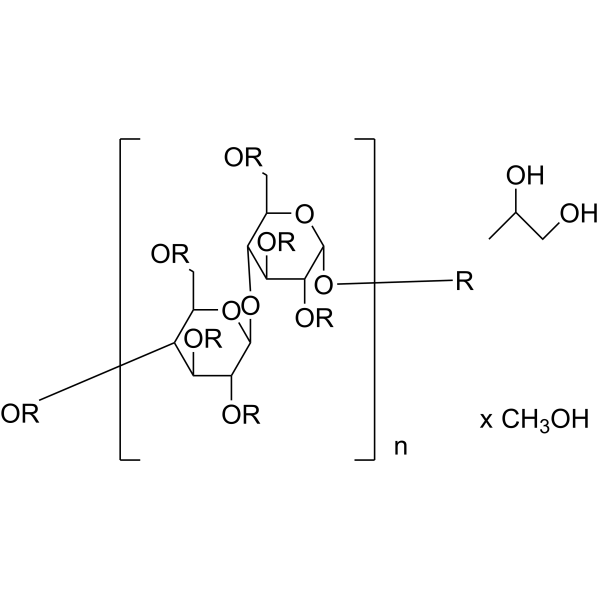 |
Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose
CAS:9004-65-3 |