| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
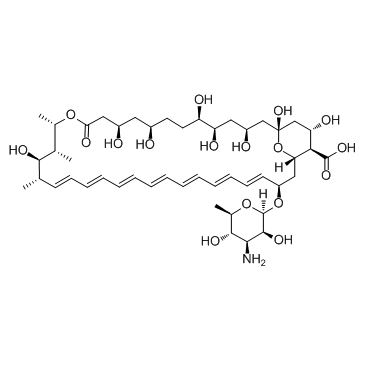 |
Amphotericin B
CAS:1397-89-3 |
|
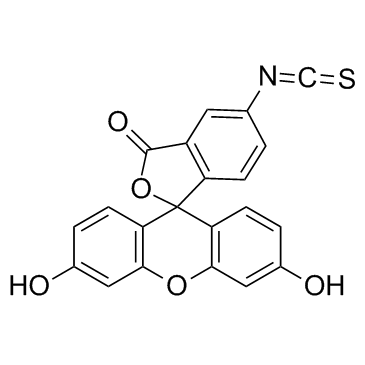 |
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
CAS:3326-32-7 |
|
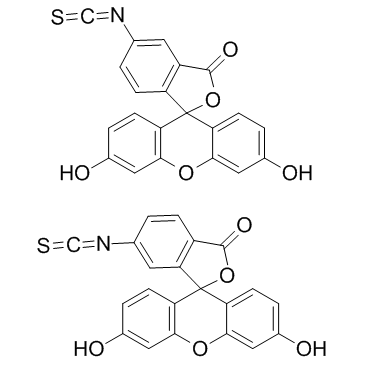 |
fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate
CAS:27072-45-3 |
|
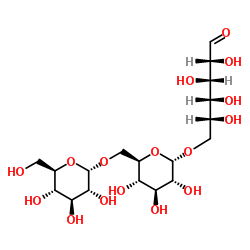 |
Dextran
CAS:9004-54-0 |
|
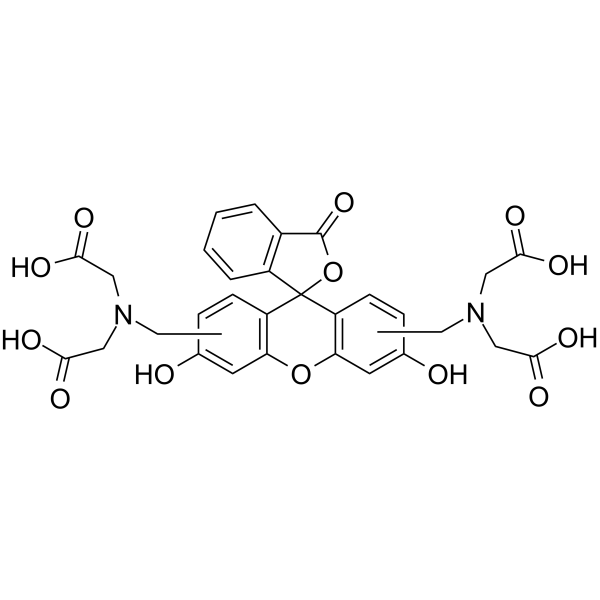 |
Calcein (mixture of isomers)
CAS:154071-48-4 |