| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
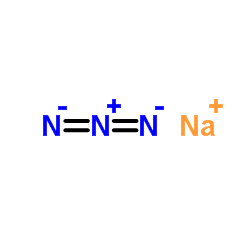 |
Sodium azide
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
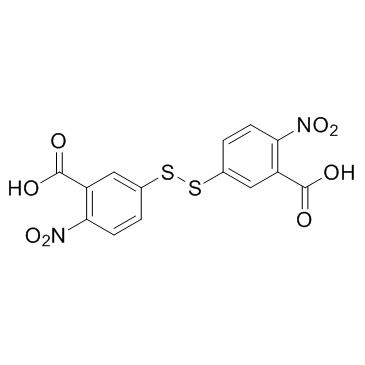 |
DTNB
CAS:69-78-3 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
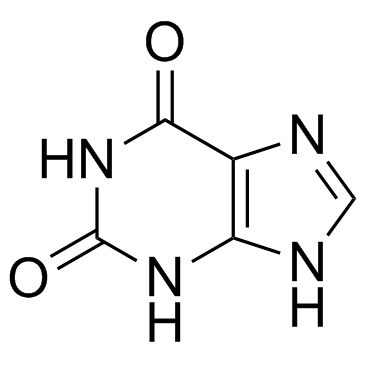 |
2,6-Dihydroxypurine
CAS:69-89-6 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
 |
L-Glutathione oxidized disodium salt
CAS:103239-24-3 |
|
 |
Cumyl hydroperoxide
CAS:80-15-9 |