| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
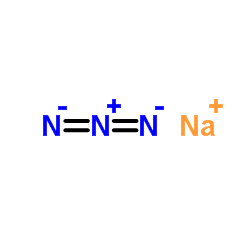 |
Sodium azide
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
0MPTP hydrochloride
CAS:23007-85-4 |
|
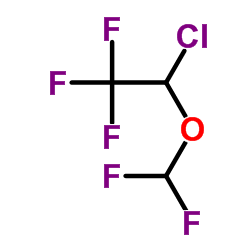 |
Isoflurane
CAS:26675-46-7 |
|
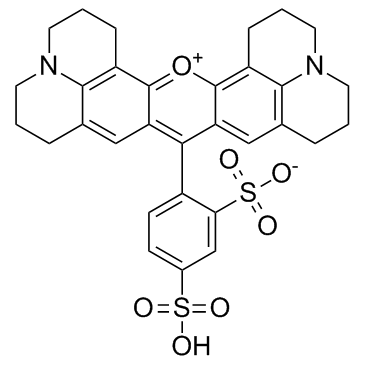 |
Sulforhodamine 101
CAS:60311-02-6 |
|
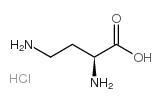 |
H-Dab.HCl
CAS:1482-98-0 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
4-(4-aminophenyl)aniline
CAS:92-87-5 |
|
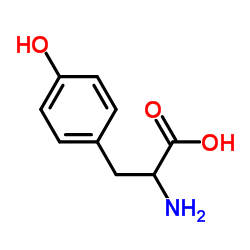 |
DL-Tyrosine
CAS:556-03-6 |