| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
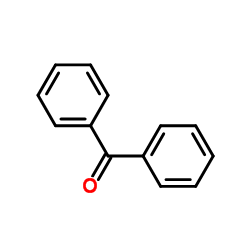 |
Benzophenone
CAS:119-61-9 |
|
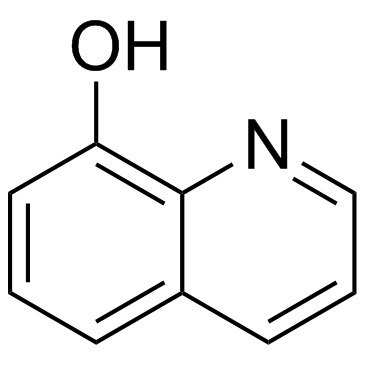 |
8-Hydroxyquinoline
CAS:148-24-3 |
|
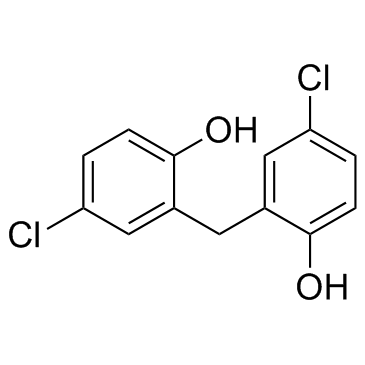 |
Dichlorophen
CAS:97-23-4 |
|
 |
Indoximod
CAS:110117-83-4 |
|
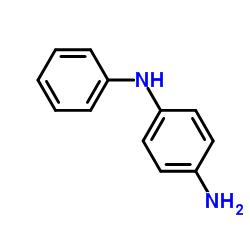 |
4-Aminodiphenylamine
CAS:101-54-2 |
|
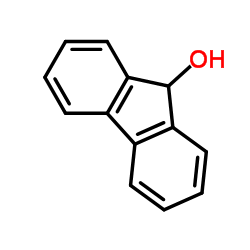 |
9-fluorenol
CAS:1689-64-1 |
|
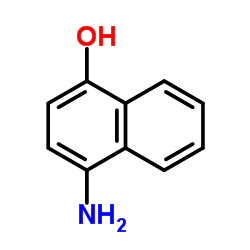 |
4-Amino-1-naphthol Hydrochloride
CAS:5959-56-8 |
|
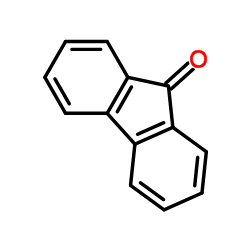 |
9-Fluorenone
CAS:486-25-9 |