| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
L-Kynurenine
CAS:2922-83-0 |
|
 |
Hippuric acid
CAS:495-69-2 |
|
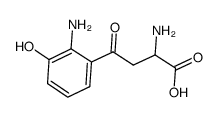 |
3-hydroxy-dl-kynurenine
CAS:2147-61-7 |