| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
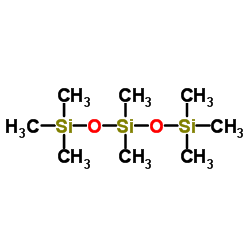 |
Octamethyltrisiloxane
CAS:107-51-7 |
|
 |
Hexamethyldisiloxane
CAS:107-46-0 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
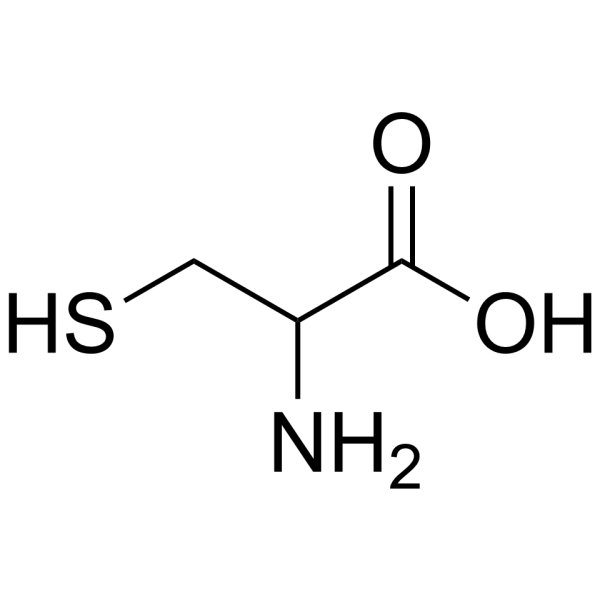 |
DL-CYSTEINE (1-13C)
CAS:3374-22-9 |
|
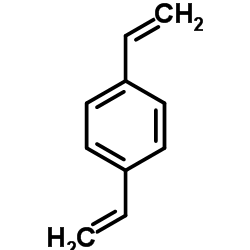 |
Divinylbenzene
CAS:1321-74-0 |
|
 |
DL-Serine
CAS:302-84-1 |
|
 |
Glycine
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
 |
DL-Phenylalanine
CAS:150-30-1 |
|
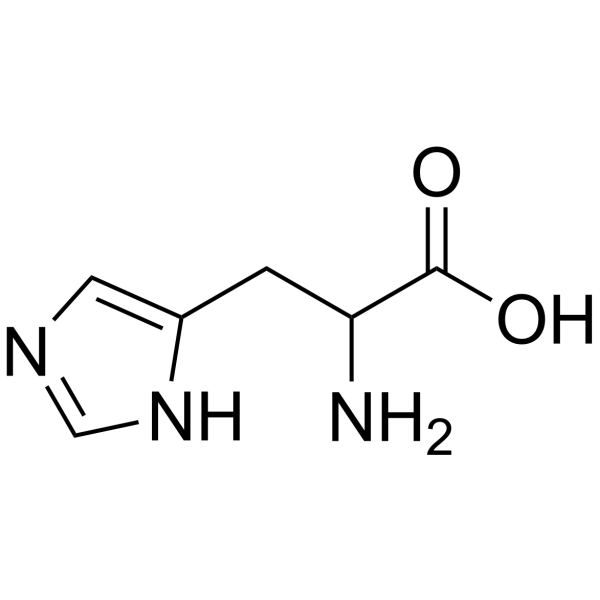 |
DL-Histidine
CAS:4998-57-6 |
|
 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |