| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
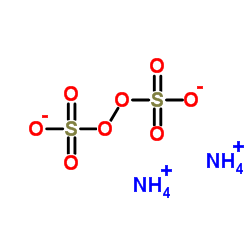 |
ammonium persulfate
CAS:7727-54-0 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
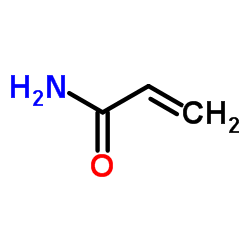 |
Acrylamide Crystals
CAS:79-06-1 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
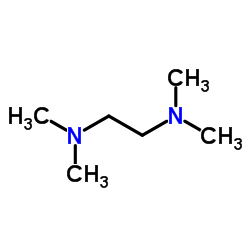 |
TMEDA
CAS:110-18-9 |
|
 |
Glycine
CAS:56-40-6 |