| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Ethanoic anhydride
CAS:108-24-7 |
|
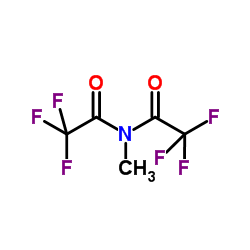 |
N-Methyl-bis(trifluoroacetamide)
CAS:685-27-8 |
|
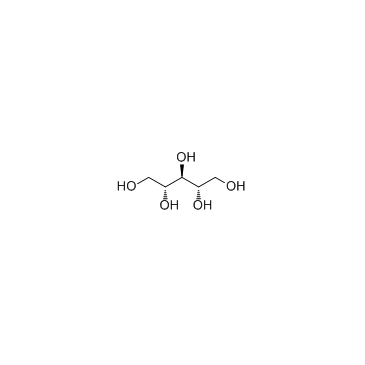 |
Ribitol
CAS:488-81-3 |
|
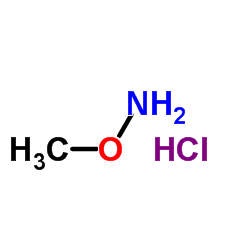 |
O-Methoxyamine HCl
CAS:593-56-6 |
|
 |
2,2,2-Trifluoroacetamide
CAS:354-38-1 |