| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
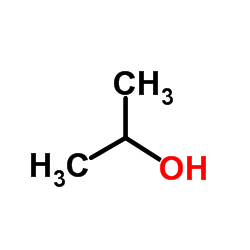 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
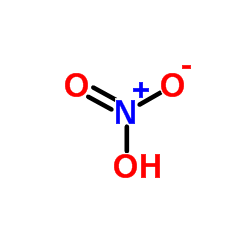 |
nitric acid
CAS:7697-37-2 |
|
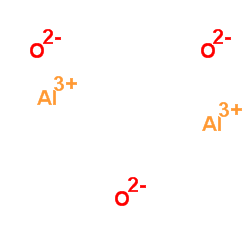 |
Aluminum oxide
CAS:1344-28-1 |
|
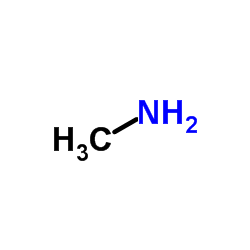 |
methylamine
CAS:74-89-5 |
|
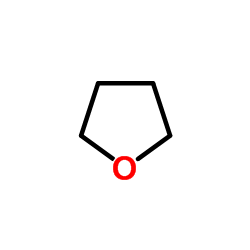 |
thf
CAS:109-99-9 |
|
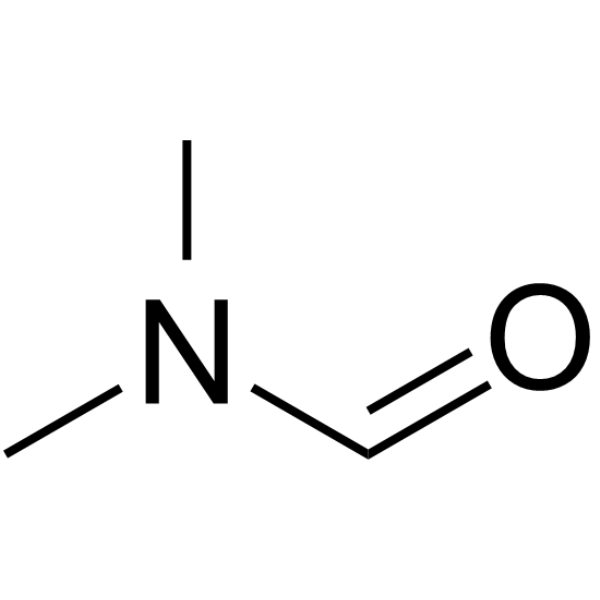 |
N,N-Dimethylformamide
CAS:68-12-2 |
|
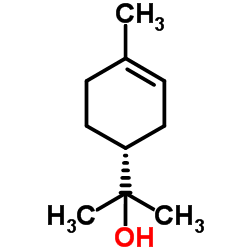 |
Terpineol
CAS:8000-41-7 |
|
 |
Hydrogen iodide
CAS:10034-85-2 |