| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
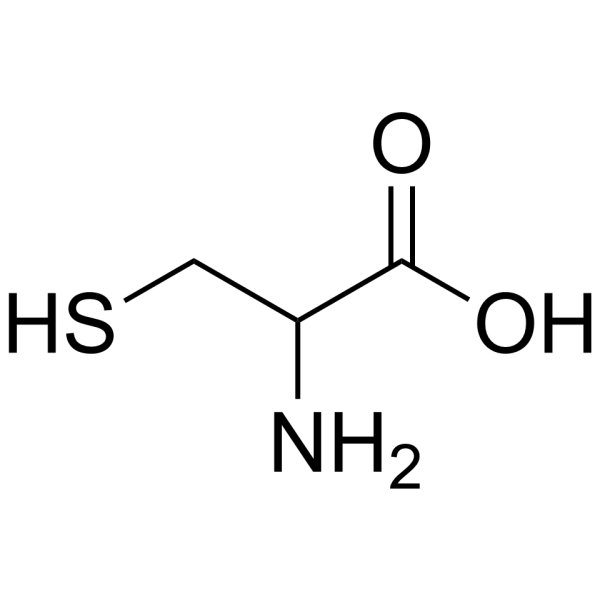 |
DL-CYSTEINE (1-13C)
CAS:3374-22-9 |
|
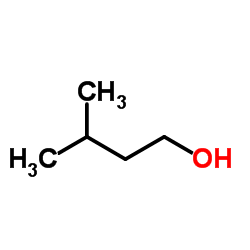 |
3-Methyl-1-butanol
CAS:123-51-3 |
|
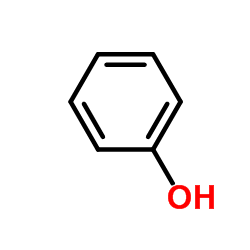 |
Phenol
CAS:108-95-2 |
|
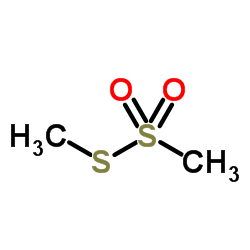 |
Methyl Methanethiosulfonate
CAS:2949-92-0 |