| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
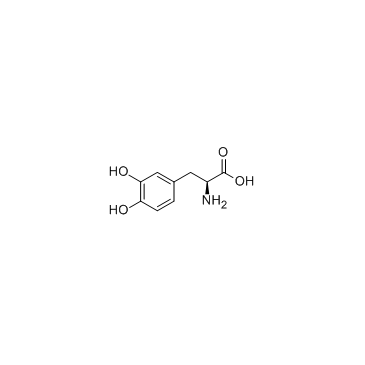 |
Levodopa
CAS:59-92-7 |
|
 |
magnesium sulfate
CAS:7487-88-9 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
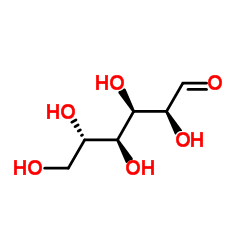 |
L-Glucose
CAS:921-60-8 |
|
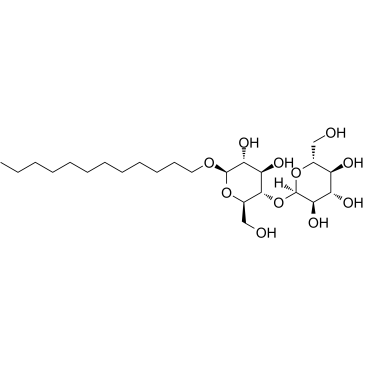 |
n-Dodecyl-beta-D-maltoside
CAS:69227-93-6 |
|
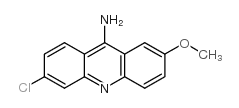 |
9-AMINO-6-CHLORO-2-METHOXYACRIDINE
CAS:3548-09-2 |