| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
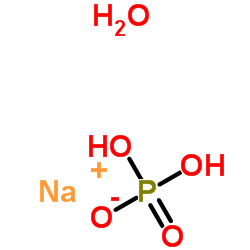 |
Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate
CAS:10049-21-5 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
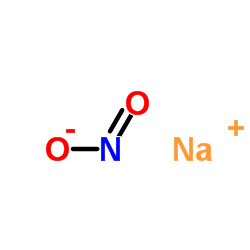 |
Sodium nitrite
CAS:7632-00-0 |
|
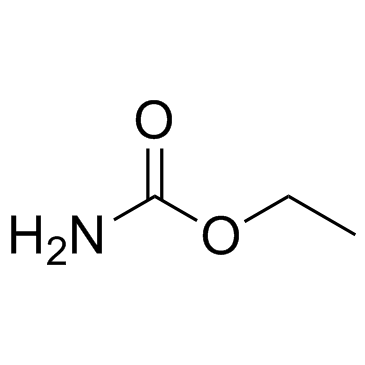 |
Urethane
CAS:51-79-6 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
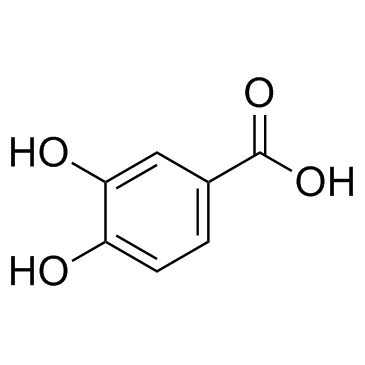 |
protocatechuic acid
CAS:99-50-3 |
|
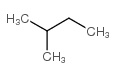 |
isopentane
CAS:78-78-4 |
|
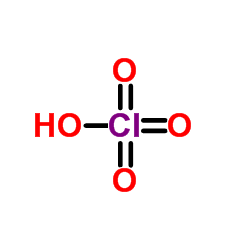 |
PERCHLORIC ACID
CAS:7601-90-3 |