| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
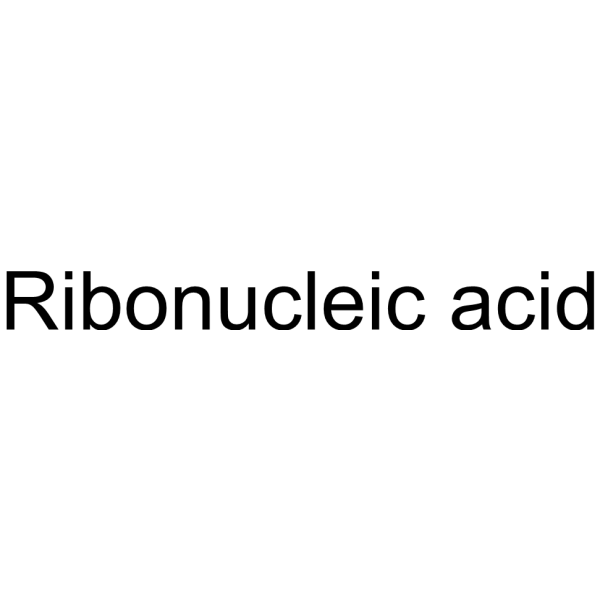 |
Ribonucleic acid
CAS:63231-63-0 |
|
 |
Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus enzyme
CAS:9068-38-6 |