| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
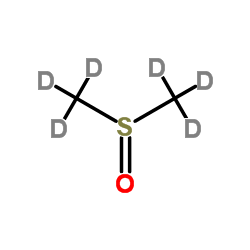 |
DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE-D6
CAS:2206-27-1 |
|
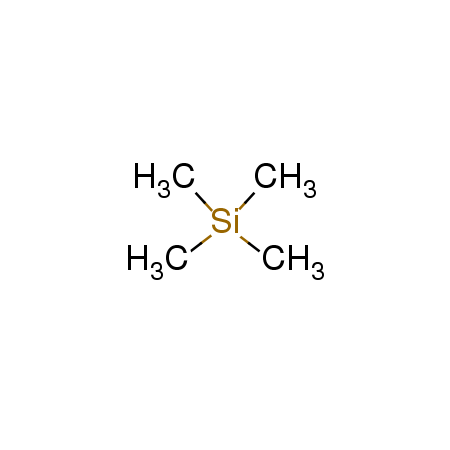 |
TMS
CAS:75-76-3 |
|
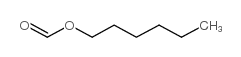 |
hexyl formate
CAS:629-33-4 |
|
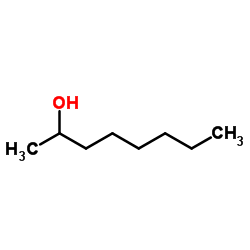 |
Octan-2-ol
CAS:123-96-6 |